Single Page SEO: 9 Steps to Rank 1-Page Websites
Written by
Ernest Bogore
CEO
Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine
Content Marketing Expert

In this article, you'll learn how to optimize a single-page website to rank in both traditional search and AI-powered search engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity.
You'll get a 9-step framework for single-page SEO, real examples of one-page sites that rank, specific tools to use at each step, and guidance on making your single page visible where your audience actually searches—whether that's Google, ChatGPT, Claude, or Perplexity.
This guide covers 83,670 citations worth of research on how AI engines cite sources differently from traditional search, and how that affects your single-page strategy.
Table of Contents
What Is Single Page SEO?
Single-page SEO is the practice of optimizing one URL to rank on search engines and convert visitors—without relying on blog posts, internal pages, or complex site structures.
It's the default approach for portfolios, product launches, SaaS tools with a single offering, event pages, and app landing pages. Any situation where you have one audience, one message, and one conversion goal.
The constraint is real: you're competing against sites with hundreds of pages, extensive internal linking, and topical depth. But constraints force focus. And focus, applied correctly, wins.
Pros and Cons of Single-Page Websites for SEO
Before committing to a single-page approach, understand the tradeoffs. This isn't a matter of good vs. bad—it's about fit.
Advantages
Concentrated link equity. Every backlink points to the same URL. Unlike multi-page sites where link juice spreads across dozens of URLs, single-page sites compound authority in one place. For competitive keywords, this concentration can outperform larger sites with diluted link profiles.
Faster load times. Fewer assets, simpler architecture, faster initial render. With Core Web Vitals influencing rankings, this technical advantage matters. Single-page sites typically achieve sub-2-second load times without heavy optimization work.
Focused user experience. No navigation decisions. No getting lost. Users scroll through a deliberate narrative, which typically improves engagement metrics. Better engagement signals contribute to ranking stability.
Lower maintenance overhead. One page to update, test, and monitor. For solo founders or lean teams, this simplicity frees resources for promotion and conversion optimization instead of content management.
AI citation potential. AI search engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity cite sources differently than Google ranks them. A well-structured single page with clear, authoritative information can earn citations in AI-generated answers even without the domain authority traditional SEO requires.
Disadvantages
Limited keyword coverage. One page can realistically target one primary keyword and a handful of related terms. You can't rank for "CRM software," "CRM pricing," and "CRM implementation guide" with a single URL. Multi-topic strategies require multi-page sites.
No internal linking. Internal links are a powerful ranking factor that single-page sites can't leverage. You'll depend more heavily on external backlinks, which are harder to control and slower to build.
Harder to build topical authority. Search engines reward sites that demonstrate expertise across related topics. A single page can't establish the depth that signals authority in competitive niches.
Analytics complexity. Standard page-level analytics don't work. You'll need event tracking or virtual pageviews to understand how users engage with different sections—which requires additional setup in Google Analytics 4.
Growth ceiling. Single-page sites work for narrow use cases. If your business grows to serve multiple audiences or products, you'll eventually need additional pages. Plan for this transition from the start.
9 Steps to Rank a Single-Page Website
These nine steps cover everything from keyword selection to conversion optimization. Each step includes the traditional SEO approach plus considerations for AI search visibility, since 30-40% of users now research products using ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Claude alongside (or instead of) Google.
Step 1: Choose a Focused Primary Keyword
Your primary keyword determines everything else. For single-page sites, specificity beats volume. A 500-search-per-month keyword that perfectly matches your offering will outperform a 10,000-search keyword where you're competing against enterprise sites.
Start with Google Autocomplete. Type your core topic and note what Google suggests. These suggestions reflect real search behavior. Look for long-tail variations that add specificity: "UX portfolio" vs. "UX portfolio for product designers" vs. "UX portfolio examples SaaS."
![[SCREENSHOT: Google Autocomplete showing suggestions for a niche keyword, with search volume visible from Keyword Surfer extension]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515745-blobid0.png)
Validate with keyword research tools. Use Ahrefs, Semrush, or the free Keyword Surfer Chrome extension to check search volume and keyword difficulty. For single-page sites, prioritize keywords with difficulty under 40 and clear commercial or informational intent.
![[SCREENSHOT: Ahrefs or Keyword Surfer showing keyword metrics—volume, difficulty, and parent topic]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515745-blobid1.png)
Check the SERP manually. Search your target keyword and examine the top 10 results. What content format does Google prioritize—landing pages, blog posts, tools? Can a single-page site realistically compete? If the top results are all comprehensive guides with 3,000+ words, a single landing page may struggle.
Map 3-5 secondary keywords. Your single page should target one primary keyword but can support several secondary terms. Pull these from Google's "People also ask" and "Related searches" sections. Each secondary keyword becomes the focus of one section on your page.
![[SCREENSHOT: Google "People also ask" section showing related questions for the target keyword]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515760-blobid2.png)
Finding Keywords for AI Search Visibility
AI search engines like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity don't use keywords the same way Google does. Users ask questions in natural language: "What's the best portfolio builder for UX designers?" instead of typing "UX portfolio builder."
This means your keyword research needs a second layer: prompt research.
Test prompts in AI engines directly. Open ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity. Ask the questions your target audience would ask. Note which brands get mentioned, which sources get cited, and how answers are structured. This reveals what AI engines consider authoritative for your topic.
Use prompt suggestion tools. Analyze AI's prompt suggestion feature generates AI search queries based on your tracked competitors. These suggestions show what questions people actually ask AI engines about your category—queries that won't appear in traditional keyword tools.
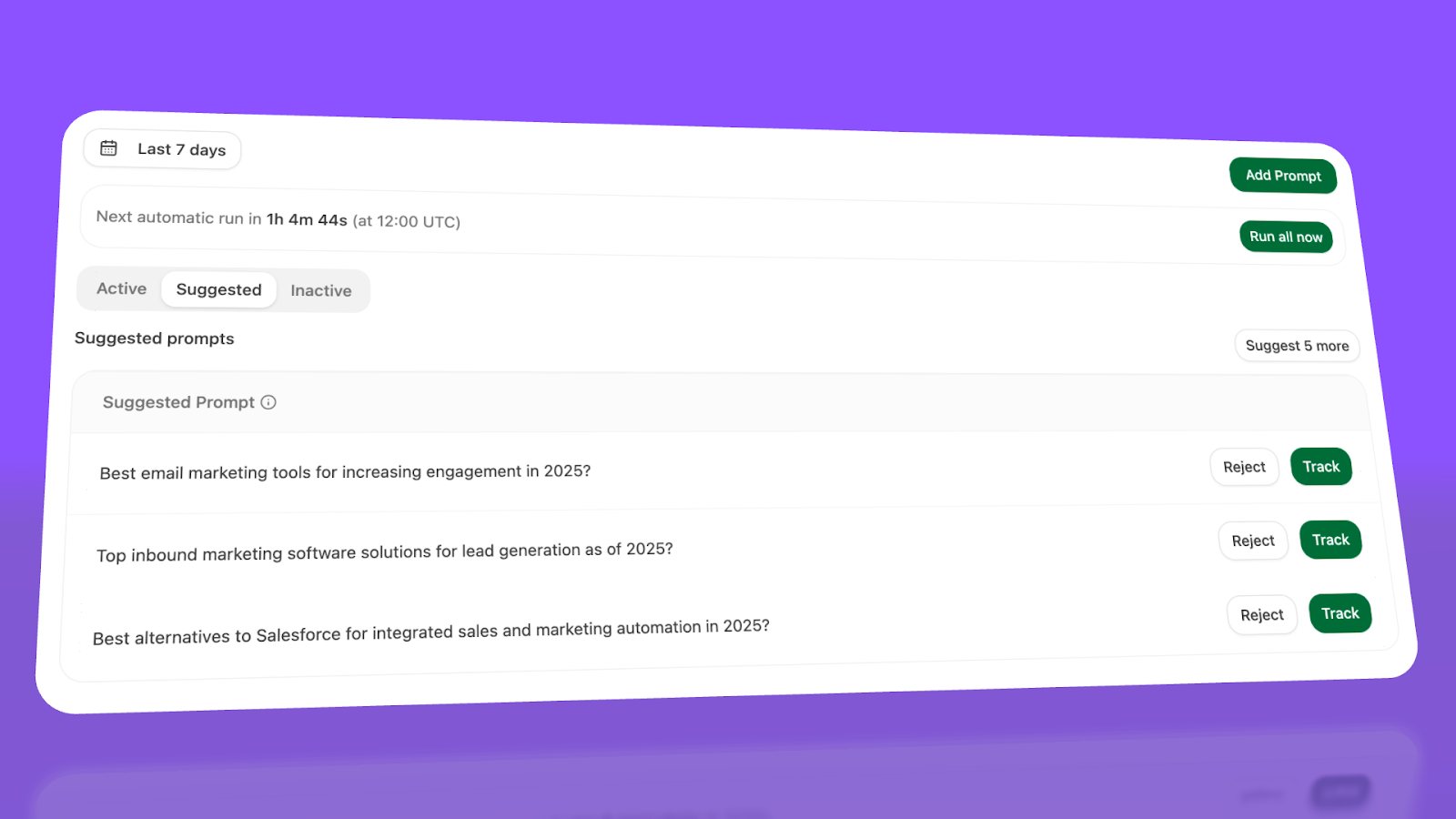
Track the prompts that matter to your business. Add 10-20 prompts that represent how your ideal customers search. Run them daily to monitor your visibility, competitors' visibility, and sentiment over time.
![[SCREENSHOT: Analyze AI prompt tracking dashboard showing visibility, sentiment, and position metrics—use Prompts.png from project files]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515766-blobid4.png)
Step 2: Structure Your Page with Clear Sections
Single-page sites live or die by structure. Without multiple URLs to organize content, you need impeccable on-page organization that helps both users and search engines understand your content hierarchy.
Use H2 headings for major sections. Each H2 should address a distinct topic or question related to your primary keyword. Think of each H2 as a mini-landing page within your larger page. For a portfolio site, this might be: About (H2), Work (H2), Services (H2), Testimonials (H2), Contact (H2).
Use H3 headings for subsections. H3s break down H2 sections into scannable chunks. Under a "Services" H2, you might have H3s for each specific service offered. This hierarchy signals content organization to search engines.
Include keywords in headings naturally. Your primary keyword should appear in at least one H2. Secondary keywords can appear in other H2s or H3s. Don't force it—awkward keyword placement hurts readability and can trigger over-optimization penalties.
Add anchor links for navigation. Create a sticky navigation menu with links to each H2 section. This improves user experience (visitors can jump to what matters) and helps search engines understand your page structure. Mobile users particularly benefit from anchor navigation.
![[SCREENSHOT: Example single-page site showing sticky navigation with anchor links—like the Norma HR example with jump links for Benefits, Pricing, FAQ, etc.]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515773-blobid5.png)
Lead each section with a benefit or answer. Don't make visitors read three paragraphs to understand what a section is about. Front-load the value. If your "Pricing" section's key message is "Start free, pay when you scale," put that in the H2 or immediately following.
Step 3: Craft a Title Tag and Meta Description That Earn Clicks
Your title tag and meta description are your page's advertisement in search results. They determine click-through rate—and click-through rate influences rankings.
Title tag formula: [Primary Keyword] – [Unique Value Proposition] | [Brand]. Keep it under 60 characters so Google displays the full title. Example: "UX Portfolio Builder – Ship in 10 Minutes | Folio."
Lead with your keyword. Search engines weight the beginning of title tags more heavily. If your keyword is "single page website builder," don't bury it after your brand name.
Meta description formula: [What it is] + [Key benefit] + [Proof point or specificity] + [Call to action]. Keep it under 155 characters. Example: "Create a stunning UX portfolio in minutes. Used by 10,000+ designers. No coding required. Start free today."
Use active voice. "Build your portfolio" beats "Portfolios can be built." Active voice creates urgency and clarity.
Test before publishing. Use Portent's SERP Preview Tool or Mangools' SERP Simulator to see exactly how your title and description will appear in search results. Catch truncation before it happens.
![[SCREENSHOT: SERP preview tool showing a well-optimized title and meta description vs. a truncated one]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515773-blobid6.png)
Step 4: Optimize Page Speed and Core Web Vitals
Single-page sites have a natural advantage here: fewer assets, simpler architecture, faster loads. But that advantage disappears if you load heavy images, unnecessary scripts, or bloated frameworks.
Target these Core Web Vitals benchmarks:
-
LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): Under 2.5 seconds. This measures how quickly your main content loads. For single-page sites, your hero section usually determines LCP.
-
INP (Interaction to Next Paint): Under 200ms. This measures responsiveness to user input. Heavy JavaScript delays INP.
-
CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift): Under 0.1. This measures visual stability. Images without defined dimensions cause layout shifts.
Compress and format images correctly. Use WebP or AVIF formats instead of JPEG or PNG. Compress with TinyPNG or Squoosh. Set explicit width and height attributes to prevent layout shift. A single unoptimized hero image can tank your LCP.
![[SCREENSHOT: PageSpeed Insights results showing Core Web Vitals scores—ideally all passing]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515782-blobid7.png)
Minimize JavaScript. Every third-party script—analytics, chat widgets, tracking pixels—adds load time. Audit what's necessary. Defer non-critical scripts. For simple single-page sites, you may not need a JavaScript framework at all.
Use a CDN. Content delivery networks serve assets from servers geographically closer to users. Cloudflare's free tier handles most single-page site needs.
Test with real tools. PageSpeed Insights gives you Core Web Vitals data from real Chrome users. GTmetrix provides waterfall charts showing exactly what loads when. Test on mobile—that's where most performance issues surface.
Step 5: Write for Readability and Scannability
Users scroll. They skim. They decide in seconds whether your page deserves their attention. Your writing needs to accommodate this behavior while still delivering substance.
Keep paragraphs short. 2-4 lines maximum. Long text blocks trigger "wall of text" avoidance. Single sentences can be their own paragraphs when they deserve emphasis.
Use bold for key phrases. Bold text creates visual anchors. Scanners' eyes jump to bolded words. Make sure those words convey your key messages.
Front-load sentences. Put the most important information at the beginning of sentences and paragraphs. Journalists call this the "inverted pyramid." Web writers call it essential.
Write at an 8th-grade level. Use Hemingway Editor to check readability. Simpler sentences aren't dumbed down—they're accessible. Even technical audiences prefer clarity.
Add CTAs throughout, not just at the end. Single-page sites are long scrolls. Users who are convinced after 30% of the page need a way to act. Place secondary CTAs after major value propositions.
![[SCREENSHOT: Example of a well-formatted single-page section with short paragraphs, bold key phrases, and a mid-page CTA]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515784-blobid8.png)
Step 6: Implement Schema Markup
Schema markup helps search engines understand what your page is about. For single-page sites without rich content hierarchies, schema provides the context that page structure can't.
Organization schema is essential. This tells search engines your brand name, logo, contact information, and social profiles. It's the foundation for knowledge panel eligibility and brand searches.
Add Product or SoftwareApplication schema if applicable. For SaaS landing pages or product launches, product schema can trigger rich snippets showing pricing, ratings, and availability directly in search results.
Use FAQ schema for common questions. If your single page includes an FAQ section, FAQ schema can earn additional SERP real estate. Each question-answer pair can appear directly in search results.
Generate with free tools. Merkle's Schema Markup Generator or Google's Structured Data Markup Helper creates JSON-LD code you can paste directly into your page's <head> section.
Validate before publishing. Google's Rich Results Test catches schema errors before they affect your site. Test after implementation and after any page changes.
![[SCREENSHOT: Google Rich Results Test showing valid schema markup with eligible rich result types]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515787-blobid9.jpg)
Schema and AI Search Visibility
Schema markup matters for AI search, too. AI engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity parse structured data to understand entities, relationships, and facts about your brand.
Clear Organization schema helps AI engines correctly identify and describe your brand. SameAs properties linking to your social profiles, Wikipedia page (if you have one), and Crunchbase entry help establish entity connections that AI models use for knowledge graphs.
If AI engines are citing incorrect information about your brand, schema markup is your first line of defense for providing authoritative, machine-readable corrections.
Step 7: Add Visuals That Support Your Message
Visuals aren't decoration. They're evidence, clarification, and engagement drivers. On single-page sites, where you're asking users to scroll through a lot of content, visuals break up text and maintain attention.
Use product screenshots and UI previews. If you're selling software, show it. Screenshots demonstrate value faster than paragraphs of description. Annotated screenshots that highlight specific features perform even better.
Include social proof visually. Testimonial sections with customer photos and company logos convert better than text-only quotes. Trust badges and client logos should be visible, not buried.
Optimize every image for SEO. Descriptive file names ("ux-portfolio-builder-dashboard.png" not "IMG_1234.png"). Alt text that includes relevant keywords while accurately describing the image. Proper compression for fast loading.
Avoid generic stock photos. Users recognize stock imagery and discount it. If you must use stock, choose images that feel specific to your context. Better: create original visuals, even simple ones.
Place visuals near relevant content. Images should support adjacent text, not float randomly. The relationship between text and image should be obvious.
![[SCREENSHOT: Example single-page site section showing product screenshot with annotation callouts explaining key features]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515792-blobid10.png)
Step 8: Build Backlinks Strategically
Without internal linking, single-page sites depend almost entirely on external backlinks for authority. This makes link building more critical—and more challenging—than for multi-page sites.
Create something worth linking to. Generic landing pages don't earn links. To attract links organically, your page needs a unique angle: a useful tool, impressive design, original research, or a strong point of view that others want to reference.
Submit to curated directories. Design showcases like One Page Love and Land-Book specifically feature single-page websites. SaaS directories like Product Hunt, BetaList, and Startup Resources provide both exposure and backlinks.
Pitch relevant blogs and newsletters. Find publications that cover your space. Personalize outreach. Explain why your page would interest their readers. Generic "please link to us" emails get deleted.
Engage in communities. Reddit communities like r/web_design, r/SideProject, and niche-specific subreddits can drive traffic and occasionally links. Contribute value first—don't just drop links.
Create embeddable assets. Badges, widgets, or tools that others can embed on their sites—with a link back to you—scale link building beyond manual outreach.
Building Visibility for AI Citations
AI search engines cite sources differently than Google ranks pages. Our analysis of 83,670 AI citations found that 83% of AI citations come from third-party sources, not brand websites directly.
This means getting mentioned on authoritative third-party sites—review platforms, industry publications, comparison articles—may matter more for AI visibility than building links to your own domain.
Track which sources AI engines cite for your category. Use Analyze AI's citation analytics to see which domains get cited most frequently for prompts related to your business. Then prioritize getting mentioned on those specific sites.
![[SCREENSHOT: Analyze AI Top Sources dashboard showing most-cited domains with citation counts—use Top_Sources.png from project files]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515796-blobid11.png)
Monitor where competitors get cited. If AI engines consistently cite a competitor's reviews on G2 or mentions in TechCrunch, that tells you where to focus your PR and earned media efforts.
![[SCREENSHOT: Analyze AI citation analytics showing which URLs and domains are cited for specific prompts—use Citation_Analytics.png from project files]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515802-blobid12.png)
Step 9: Optimize Calls-to-Action for Conversion
Traffic means nothing without conversion. Single-page sites have one advantage here: every visitor sees your CTA. No navigation confusion, no getting lost. But you have to make that CTA count.
Make CTAs visually prominent. Buttons should contrast with surrounding colors. Size should be large enough to tap easily on mobile. Placement should be obvious—don't make users hunt.
Use action-oriented button text. "Start Free Trial" beats "Submit." "Get Your Portfolio" beats "Sign Up." Specific actions outperform generic commands.
Add supporting text near CTAs. A one-line value proposition directly above the button reinforces why users should click. "Join 10,000+ designers" or "No credit card required" addresses common hesitations.
Include social proof near conversion points. Testimonials, user counts, or client logos positioned near CTAs boost conversion rates. Users look for validation right before committing.
Place CTAs throughout the page. Not just at the bottom. Add CTAs in the hero section, after major value propositions, and in a sticky header or floating button for mobile.
Add a "Back to Top" option. For long single-page sites, help users navigate back to the beginning or to specific sections. Smooth scroll enhances the experience.
![[SCREENSHOT: Example CTA section with prominent button, supporting value proposition text, and nearby testimonials or trust badges]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515806-blobid13.png)
Measuring Results: Traditional Search and AI Search
After implementing these optimizations, you need to track whether they're working. Single-page sites require slightly different measurement approaches for both traditional and AI search.
Tracking Traditional Search Performance
Google Search Console shows your impressions, clicks, average position, and click-through rate for specific keywords. Monitor your primary keyword's position weekly. Watch for seasonal patterns and algorithm update impacts.
Google Analytics 4 tracks on-page behavior. For single-page sites, set up scroll depth tracking and event tracking for section views and CTA clicks. Without this setup, all you'll see is a single pageview—no insight into engagement.
Rank tracking tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, or SE Ranking provide daily position monitoring and competitor comparisons. Track your primary keyword plus 5-10 secondary keywords.
Tracking AI Search Performance
AI search visibility requires different tools. Google Search Console doesn't show whether ChatGPT mentioned your brand. GA4 can track AI referral traffic, but you need to know what to look for.
Track AI referral traffic in GA4. Filter traffic by source to see visits from ChatGPT (chat.openai.com), Perplexity (perplexity.ai), Claude (claude.ai), and other AI engines. Our data shows AI referral traffic growing 300%+ year-over-year for many B2B sites.
![[SCREENSHOT: Analyze AI AI Referral Traffic dashboard showing sessions from different AI engines with trend data—use AI_Referral_Traffic.png from project files]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515810-blobid14.png)
See which pages receive AI traffic. For single-page sites, this is straightforward—your one page. But tracking the volume and source helps identify which AI engines send the most qualified visitors.
![[SCREENSHOT: Analyze AI Landing Pages from AI Search showing page-level attribution—use AI_Traffic_By_Page.png from project files]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515814-blobid15.png)
Monitor brand visibility across AI engines. Use Analyze AI's prompt tracking to see how often your brand appears in AI-generated answers, your average position, and how sentiment changes over time.
![[SCREENSHOT: Analyze AI prompt-level analytics showing visibility percentage, sentiment score, and position over time—use Prompt_Level_Analytics.png from project files]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515820-blobid16.png)
Compare performance across engines. ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity behave differently. Perplexity provides 29% more citations per mention than ChatGPT. Claude cites blog content 4x more than ChatGPT does. Understanding these differences helps you prioritize optimization efforts.
![[SCREENSHOT: Analyze AI Analytics By Engine showing breakdown of visibility and traffic by AI platform—use Analytics_By_Engine.png from project files]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515824-blobid17.png)
Finding Opportunities Where Competitors Win
The fastest way to improve visibility—in both traditional and AI search—is identifying where competitors appear and you don't.
For traditional SEO, use Ahrefs' Content Gap or Semrush's Keyword Gap tools to find keywords where competitors rank and you don't. These gaps reveal content opportunities—though for single-page sites, you may need to incorporate these keywords into existing sections rather than creating new pages.
For AI search, Analyze AI's Opportunities feature shows prompts where competitors get mentioned and your brand doesn't appear. These are high-value gaps—people are actively asking AI about your category, AI is recommending your competitors, and you're invisible.
![[SCREENSHOT: Analyze AI Opportunities dashboard showing prompts where competitors win—use Opportunities.png from project files]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515831-blobid18.png)
Track competitors systematically. Add your main competitors to monitoring. See their mention frequency, which prompts they dominate, and how their visibility changes over time.
![[SCREENSHOT: Analyze AI Competitor Overview showing tracked competitors with mention counts—use Competitor_Overview.png from project files]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/164164/1769515833-blobid19.png)
Key Takeaways
Single-page SEO works when you have a focused audience, a clear message, and one conversion goal. The constraint of a single URL forces strategic clarity that often gets diluted across larger sites.
The tradeoffs are real: limited keyword coverage, no internal linking, harder analytics. But the advantages—concentrated link equity, faster speeds, focused UX—can outweigh them for the right use cases.
Execute the fundamentals: one primary keyword, clear page structure, fast load times, compelling visuals, strategic backlinks, and conversion-optimized CTAs. These principles work whether you're optimizing for Google or for AI search engines.
Don't ignore AI search. ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity are where a growing percentage of your audience discovers solutions. Our research shows 83% of AI citations come from third-party sources—so building visibility through earned media, reviews, and authoritative mentions matters as much as optimizing your own page.
Measure both channels. Use Search Console and GA4 for traditional search performance. Use tools like Analyze AI to track AI referral traffic, brand mentions, and citation sources. What you measure, you can improve.
Single-page sites can rank. But ranking is the beginning, not the goal. The goal is traffic that converts into customers—from whatever source your audience uses to find solutions.
Tie AI visibility toqualified demand.
Measure the prompts and engines that drive real traffic, conversions, and revenue.
Similar Content You Might Want To Read
Discover more insights and perspectives on related topics

2026 SEO Content Strategy: 10-Step Breakdown

6 Ways To Search Any Website For Keywords (+ How To Find Keywords Driving AI Traffic)

Secondary Keywords: What They Are and How to Find and Use Them

Best SEO Software for 2026: Overview & How to Choose

We Analyzed 83,670 AI Citations: ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity Don't Agree on Anything
